Chapter 03. Muscle: the Primary stabilizer and mover of the skeletal System
뼈대계통의 일차적인 안정자와 운동자
뼈대 안정자(stabilizer)로서의 근육
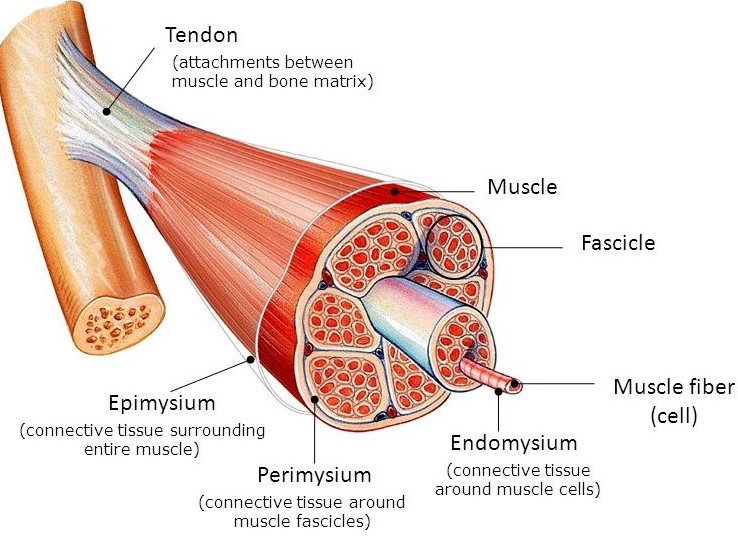

세포바깥(amiculum) 막 결합 조직
1. 근육바깥막(epimysium)
2. 근육다발막(perimysium)
a. 다발 근육 (fascicle)
b. 근섬유(muscle fiber)
3. 근육속막(endomysium)-muscle fiber를 감싸고 있는 막
a. Muscle fiber 안에 mitochondrion 과 nucleus 존재-기본단위
****Myofibril(근원섬유) myofilaments(근잔 섬유=엑틴(actin)과 미오신(myosin))****
Muscle Morphology(형태학)

*방추근육 과 깃근육의 차이-근섬유의 주행방향이 중요하다
방추근육(fusiform)- 뼈와 뼈의 사이에 근육이 수직으로 되어 있는 형태,
깃근육은(bipennate muscle)뼈와 뼈의 사이에 근육이 사선방향으로 되어 있는 형태
Muscle Architecture
1. 생리학적 단면적(physiologic cross-sectional area)
단면적이 넓을수록 힘의 크기는 커진다
2. 깃각(pennation angle)
근육의 결이 사선이기 때문에 끝나는 지점의 기울기가 시작하는 지점의 기울기가 다르게 나타난다. 그러므로 뼈 사이의 근육의 힘이 전달되는 퍼센트가 각도에 따라 달라진다.
방추근육 깃각이 0도 (100%근육의 힘이 뼈로 전달이 된다)


'운동학(kinesiology)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| <운동학> -뉴먼 kinesiology 근육;능동적 장력 곡선,능동적 장력 곡선 (0) | 2021.12.04 |
|---|---|
| <운동학> -뉴먼 kinesiology 근육: 직렬, 병렬 탄성 요소,수동장력 (0) | 2021.12.03 |
| <운동학> -뉴먼 kinesiology- 관절 주위의 결합조직 (0) | 2021.12.02 |
| <운동학> -뉴먼 kinesiology ;가동관절(synovial joint) (0) | 2021.11.30 |
| <운동학> -뉴만 kinesiology -운동 역학 kinetic과 역학적 이득 (1) | 2021.11.29 |




댓글